Motivation is the driving force for human beings to perform vital societal actions. It is one of the most potent forces which can encourage humans to perform extraordinary jobs. Motivation is the force that defines the focus and commitment of a person towards any particular thing.
Motivation plays a significant role in business and Organizations. Companies spend heavily and continuously look for sources of motivation for their employees. A motivated workforce in an organization can work wonders and change the future of any company.
For these very reasons and the impact of motivation on human society, psychologists have been studying motivation for centuries. Many motivation theories help business executives understand and implement changes in their companies. We will be discussing all the major motivation theories and their constituents in detail on this page.
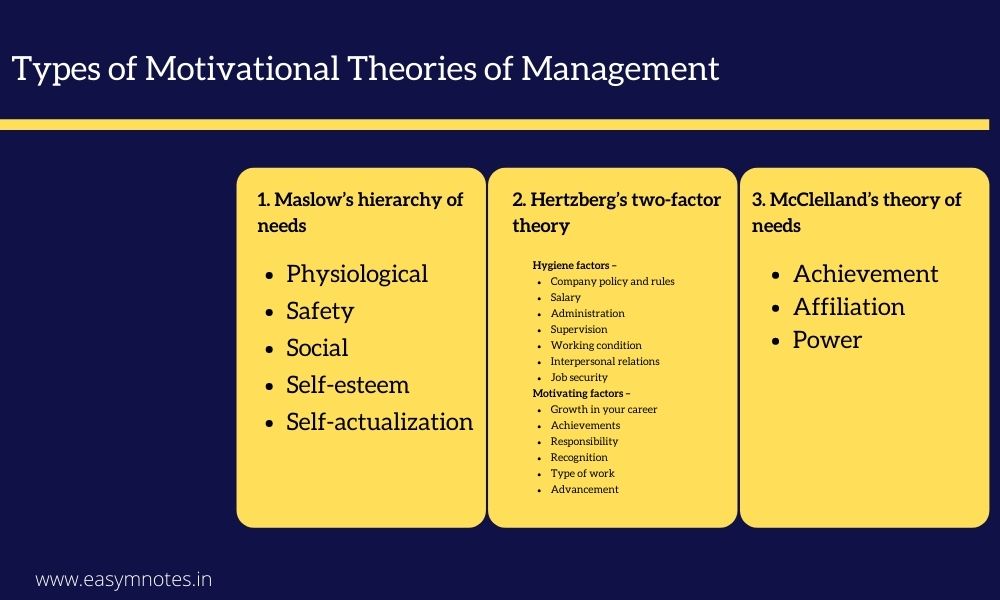
1. Maslow’s hierarchy of needs
Abraham Maslow formulated Maslow’s hierarchy of needs, explaining that a person is motivated after specific requirements are fulfilled. He divided human necessities into divisions and explained that when the needs of a particular level are satisfied, a person gets motivated to achieve the needs of the next level.
This is one of the most followed and referenced theories of motivation because of the clear concept. The hierarchy of needs as explained in theory is –
- Physiological: Physiological needs are the most basic forms of needs of humans. These include basic necessities to live, such as food, water, and shelter.
- Safety: After getting basic necessities, every human strives for safety to prevent the uncertainty of life. These needs include protection from dangers, threats, and deprivation.
- Social: After being confident of safety from all factors, humans need social acceptance in affiliation, friendship, association, etc.
- Self-esteem: After getting social approval, humans strive for self-esteem in the form of respect and recognition from society.
- Self-actualization: Self-actualization is the highest level of motivating factors for humans. In this category, humans look for opportunities for learning, growth, personal development, and creative work to feed their enthusiastic souls and needs.
2. Hertzberg’s two-factor theory
Hertzberg’s theory is divided into two sections; one being hygiene factors and the other being motivating factors. Hygiene factors are the fundamental factors necessary for every organization for the employees to work with motivation. Driving factors, on the other hand, are the extra factors that bring in the extra push for employees to put in extra effort to outperform and deliver results for the company.
Both of these factors run hand-in-hand in a company. Hygiene or motivating factors alone in a company cannot motivate the employees to perform at their peak and bring significant results.
The factors as described in theory are –
Hygiene factors –
- Company policy and rules
- Salary
- Administration
- Supervision
- Working condition
- Interpersonal relations
- Job security
Motivating factors –
- Growth in your career
- Achievements
- Responsibility
- Recognition
- Type of work
- Advancement
3. McClelland’s theory of needs
McClelland gave three straight-forwards motivating factors that apply to everyone irrespective of their age, location, gender, or other factors. The theory states that the reason for motivation for any particular individual will be one of the three factors based on their personal life experiences.
These factors are –
- Achievement – Humans are motivated to a significant extent by achievement. Accomplishing specific tasks that are high in competition and a lot of efforts are required to fulfill those tasks, which amounts to a feeling of achievement. This is the sole reason for motivation for a lot of human beings.
- Affiliation – Affiliation and social connection is a significant need for humans. Social acceptance and recognition is a significant factor of motivation for some people.
- Power – The power to have control over situations or people is a significant motivating factor. People with the motivation of power tend to work hard to achieve positions of power and authority, which grants them control and a sense of satisfaction.
- Challenges of Integrated Marketing Communication - October 27, 2024
- What Does A Business Development Manager Do? - April 8, 2024
- Let’s Know About Online Retailing, Before You Start - September 10, 2023